fclose() freezes/hangs when run inside pthread on Android 2.1
By admin | June 25, 2012
There appears to be an obscure bug that has somehow recently activated on ARMv6, non-FPU builds of VLC for Android. This has been only observed on Android 2.1 and possibly on other Android 2.x platforms with ARMv6, non-FPU builds Android 2.2. On the other hand, it works perfectly on an Android 4.0 on a NEON device (same code), so it is probably specific to Android 2.2 and 2.1 (not tested on 1.6).
The obscure bug involves hanging during a fclose() call whilst being run inside a POSIX pthread_once thread. This obscure bug was causing hanging on startup of VLC for Android on an Android 2.1, no-FPU, no-NEON device. Further testing with the Android emulator also revealed that the Android 2.1 and 2.2 emulator crashes too, suggesting a bionic bug (Android 2.3 works fine). Here is a condensed, VLC-neutral version of the code from VLC core that is specific to this problem, adapted from src/posix/linux_cpu.c:
// arm-linux-androideabi-gcc --sysroot=/opt/android-ndk-r8/platforms/android-9/arch-arm -I. -g -march=armv6j -mtune=arm1136j-s -msoft-float android.c -o android
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* getdelim and getline courtesy of VLC's compat/getdelim.c */
ssize_t getdelim(char**v1,size_t*v2,int v3,FILE*v4){char*A1=*v1;size_t A2=(A1 != NULL)?*v2:0;size_t A3 = 0;for(;;){if((A2 - A3) <= 2){A2=A2?(A2*2):256;A1=realloc(*v1,A2);if(A1 ==NULL)return-1;*v1=A1;*v2=A2;}int c=fgetc(v4);if(c==-1){if(A3==0||ferror(v4))return -1;break;}A1[A3++]=c;if(c==v3)break;}A1[A3]='\0';return A3;} ssize_t getline(char** a,size_t* b,FILE* c){return getdelim(a,b,'\n',c);}
static uint32_t cpu_flags = 0;
static void vlc_CPU_init (void) {
FILE *info = fopen ("/proc/cpuinfo", "rt");
if (info == NULL) return;
char *line = NULL;
size_t linelen = 0;
// ...irrelevant code skipped...
while (getline (&line, &linelen, info) != -1) {
// ...do stuff with the loop...
}
fclose(info); /* hangs here */
free(line);
// ...parse and set cpu_flags...
cpu_flags = 1;
}
unsigned vlc_CPU(void) {
static pthread_once_t once = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
pthread_once (&once, vlc_CPU_init);
//vlc_CPU_init();
return cpu_flags;
}
int main(void) {
if(vlc_CPU() > 0)
puts("Successful");
else
puts("Failure, or a.k.a. will never reach here");
return 0;
}
Interestingly, after debugging there are two ways to workaround this bug:
- Comment out the fclose() on line 21 above, or
- Don’t run vlc_CPU_init() inside a thread – comment out line 29 and uncomment line 30 to run vlc_CPU_init() unthreaded.
Further research – “The stdio library uses locks internally” – yields that this may be a bug in bionic, Android’s own custom implementation of libc as well as pthreads. So far, the fact that fclose() works successfully if not run inside a pthread, as well as the knowledge that stdio has internal locks, may suggest a bug in the bionic implementation on Android 2.2 / 2.1 and below.
See also http://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=5116.
Topics: Linux | 13 Comments »
Enabling icons in Qt4 apps on GNOME / GTK
By admin | June 3, 2012
By default on the latest versions of Debian and Ubuntu, the gconf preferences “/desktop/gnome/interface/menus_have_icons” and “/desktop/gnome/interface/buttons_have_icons” are set to false by default. Despite this, GTK2 and GTK3 applications both display icons next to their menus by default. However, Qt4-based applications such as VLC media player don’t display icons. To fix this:
gconftool --type boolean --set /desktop/gnome/interface/buttons_have_icons true gconftool --type boolean --set /desktop/gnome/interface/menus_have_icons true
Or, open gconf-editor and set both “/desktop/gnome/interface/menus_have_icons” and “/desktop/gnome/interface/buttons_have_icons” to true.
References
- http://crunchbanglinux.org/forums/post/195036/#p195036
- https://bbs.archlinux.org/viewtopic.php?pid=940213#p940213
Topics: Linux | 15 Comments »
Set Debian to gksudo / sudo mode instead of su-to-root
By admin | May 30, 2012
gconftool --type bool --set /apps/gksu/sudo-mode true
Or open gconf-editor and set /apps/gksu/sudo-mode to true. This way, you don’t have to set an insecure root password.
Topics: Linux | 10 Comments »
Creating Debian packages (properly) using debhelper
By admin | April 28, 2012
# change these to fit your name/e-mail address export DEBEMAIL="john.smith@fanboys.example.com" export DEBFULLNAME="John Smith" wget http://www.example.com/pub/example-2.0.1.tar.gz tar zxvf example-2.0.1.tar.gz cd example-2.0.1 dh_make -f ../example-2.0.1.tar.gz
Now, open up debian/control and modify the section field to fit one of the valid Debian sections. Then, the Build-Depends field should have whatever packages you need – minimally it should have debhelper (>= 7.0.50~), dh-buildinfo, dh-autoreconf (if you need it), along with any libraries your application will need. Set the Homepage field to be the URL of your software’s homepage on the Internet.
Once you are happy with that you can modify your package’s fields, right below the source section. Set the Architechture (i386, amd64, or etc), add Depends (Depends: ${shlibs:Depends}, ${misc:Depends} should work in most cases, because dh_shlibdeps is called). Finally, modify the package description.
A sample debian/control file:
Source: example
Section: misc
Priority: optional
Maintainer: John Smith
Build-Depends: debhelper (>= 7.0.50~),
dh-buildinfo,
dh-autoreconf,
libogg-dev
Standards-Version: 3.8.4
Homepage: http://www.example.org/
Vcs-Git: git://git.example.org/example.git
Vcs-Browser: http://git.example.org/?p=example.git;a=summary
Package: example
Architecture: i386
Depends: ${shlibs:Depends}, ${misc:Depends}
Description: Awesome example application
Example is an awesome example application. It provides examples to do many things.
.
Example can also be used as an excuse to not learn how to make examples.
A sample debian/rules file:
#!/usr/bin/make -f # -*- makefile -*- # Sample debian/rules that uses debhelper. # This file was originally written by Joey Hess and Craig Small. # As a special exception, when this file is copied by dh-make into a # dh-make output file, you may use that output file without restriction. # This special exception was added by Craig Small in version 0.37 of dh-make. # Uncomment this to turn on verbose mode. #export DH_VERBOSE=1 build: ./configure --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc --enable-ogg --enable-the-force --disable-stuff --blah-blah=blah make binary: dh_testroot dh_auto_install dh_shlibdeps dh_installdeb dh_gencontrol dh_md5sums dh_builddeb %: dh $@
To build the package (assuming everything compiles correctly):
dpkg-buildpackage -nc -us -uc -ivolatile_build_folder/
Explanation:
-nc means don’t clean (saves you time in case an error occurs)
-us and -uc mean unsigned source and unsigned changes recently, not useful if you are not official maintainer
-i means don’t consider this folder when making diff archive (to avoid dpkg-source: error: unrepresentable changes to source)
After this process is complete, the built .deb file can be found in the folder above the source folder.
Useful links:
- Debian New Maintainers’ Guide
- dpkg-shlibdeps – calculates shared library dependencies
- Unable to setup dpkg build environment
- dpkg-buildpackage
- HOWTO debian, cheat sheet
Topics: Linux | 15 Comments »
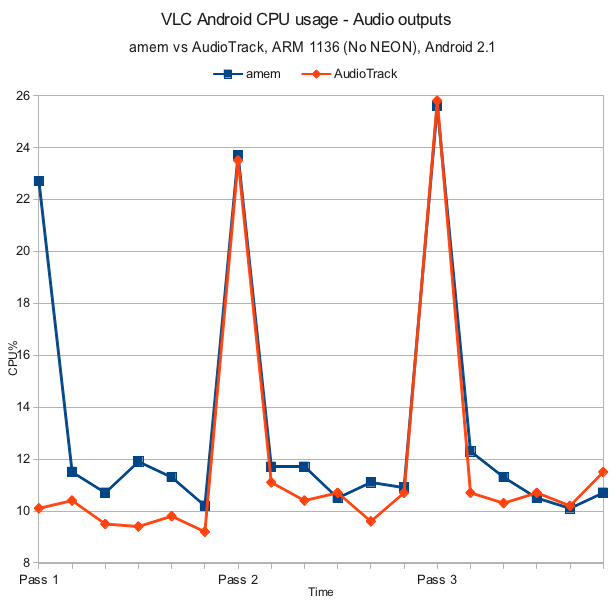
Android native AudioTrack vs amem performance
By admin | March 11, 2012
VLC for Android pre-alpha benchmarks (March 11, 2012) for two audio outputs. Specs and method are the same as in the audio benchmarks.
Sample
First 30 seconds of testfile.mp3
Results
| amem Mean: 13.24% Median: 11.30% Mode: 10.7% |
Native AudioTrack Mean: 11.87% Median: 10.40% Mode: 10.7% |
amem
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND Pass 1: D/vlc ( 3253): using audio output module "amem" 3253 957 10076 S 163m 88.3 0 22.7 org.videolan.vlc 3253 957 10076 S 161m 87.2 0 11.5 org.videolan.vlc 3253 957 10076 S 161m 87.2 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc 3253 957 10076 S 161m 87.2 0 11.9 org.videolan.vlc 3253 957 10076 S 161m 87.2 0 11.3 org.videolan.vlc 3253 957 10076 S 161m 87.2 0 10.2 org.videolan.vlc Pass 2: D/vlc ( 3366): using audio output module "amem" 3366 957 10076 R 164m 88.7 0 23.7 org.videolan.vlc 3366 957 10076 S 161m 87.5 0 11.7 org.videolan.vlc 3366 957 10076 S 161m 87.5 0 11.7 org.videolan.vlc 3366 957 10076 S 161m 87.5 0 10.5 org.videolan.vlc 3366 957 10076 S 161m 87.5 0 11.1 org.videolan.vlc 3366 957 10076 S 161m 87.5 0 10.9 org.videolan.vlc Pass 3: D/vlc ( 3590): using audio output module "amem" 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 25.6 org.videolan.vlc 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 12.3 org.videolan.vlc 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 11.3 org.videolan.vlc 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 10.5 org.videolan.vlc 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 10.1 org.videolan.vlc 3590 957 10076 S 164m 89.1 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc
AudioTrack
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND Pass 1: D/vlc ( 2835): using audio output module "android_audiotrack" 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 10.1 org.videolan.vlc 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 10.4 org.videolan.vlc 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 9.5 org.videolan.vlc 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 9.4 org.videolan.vlc 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 9.8 org.videolan.vlc 2835 957 10076 S 159m 86.0 0 9.2 org.videolan.vlc Pass 2: D/vlc ( 2948): using audio output module "android_audiotrack" 2948 957 10076 S 165m 89.5 0 23.5 org.videolan.vlc 2948 957 10076 S 164m 88.7 0 11.1 org.videolan.vlc 2948 957 10076 S 164m 88.7 0 10.4 org.videolan.vlc 2948 957 10076 S 164m 88.7 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc 2948 957 10076 S 164m 88.7 0 9.6 org.videolan.vlc 2948 957 10076 S 164m 88.7 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc Pass 3: D/vlc ( 3120): using audio output module "android_audiotrack" 3120 957 10076 S 163m 88.4 0 25.8 org.videolan.vlc 3120 957 10076 S 160m 86.8 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc 3120 957 10076 S 160m 86.8 0 10.3 org.videolan.vlc 3120 957 10076 S 160m 86.8 0 10.7 org.videolan.vlc 3120 957 10076 S 160m 86.8 0 10.2 org.videolan.vlc 3120 957 10076 S 160m 86.8 0 11.5 org.videolan.vlc
Conclusion
Although there is not much of a significant gain in either audio output, the AudioTrack output feels a bit more stable to the end-user with less glitchiness or stuttering. In addition, AudioTrack supports some formats not supported by amem output (such as mono audio).
Topics: Mobile | 12 Comments »
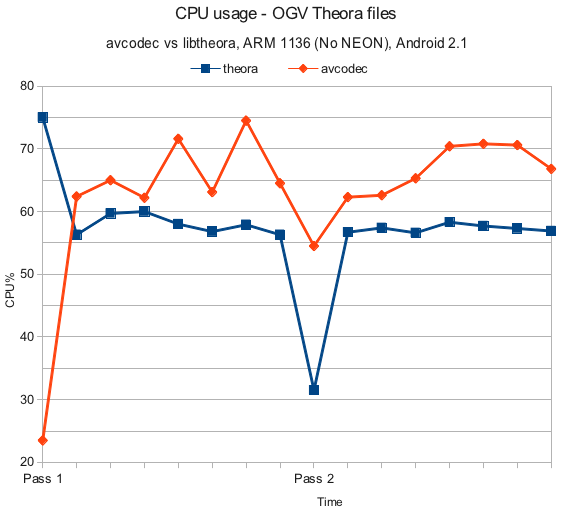
Android video codec benchmark
By admin | February 19, 2012
VLC for Android pre-alpha benchmarks (Feb 19, 2012) for various video codecs. Specs and method are the same as in the audio benchmarks.
OGV Theora sample
First 40 seconds of ogv_theora_codec_sample.ogv
Results – libtheora
| libtheora Mean: 57.02% Median: 57.35% Mode: 56.3% |
libavcodec Mean: 63.13% Median: 64.75% Mode: N/A |
ogv with libtheora
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND -A dummy --codec theora Pass 1: D/vlc (22597): using decoder module "theora" 22597 5375 10072 S 164m 89.1 0 75.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 165m 89.6 0 56.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 165m 89.6 0 59.7 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 165m 89.6 0 60.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 166m 89.9 0 58.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 167m 90.5 0 56.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 168m 91.0 0 57.9 org.videolan.vlc.android 22597 5375 10072 S 169m 91.7 0 56.3 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 2: D/vlc (22670): using decoder module "theora" 22670 5375 10072 S 161m 87.5 0 31.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 165m 89.5 0 56.7 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 166m 90.0 0 57.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 167m 90.6 0 56.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 168m 91.1 0 58.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 169m 91.7 0 57.7 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 170m 92.3 0 57.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 22670 5375 10072 S 171m 92.9 0 56.9 org.videolan.vlc.android
ogv with libavcodec
-A dummy --codec avcodec PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND Pass 1: D/vlc (22763): using decoder module "avcodec" 22763 5375 10072 S 159m 86.2 0 23.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 62.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 65.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 62.2 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 71.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 63.1 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 74.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 22763 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 64.5 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 2: D/vlc (22797): using decoder module "avcodec" 22797 5375 10072 S 162m 87.9 0 54.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.3 0 62.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 62.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 65.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 70.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 70.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 70.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 22797 5375 10072 S 165m 89.4 0 66.8 org.videolan.vlc.android
Topics: Mobile | 18 Comments »
Updated tktreecontrol deb package for Ubuntu/Debian
By admin | February 8, 2012
The version of tktreectrl in the Ubuntu repositories is, once again, a bit out of date (2.2.8). As a result, we have compiled the latest 2.4.1 version of TkTreeControl for your pleasure.
Download
Procedure
wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/tktreectrl/tktreectrl/tktreectrl-2.4.1/tktreectrl-2.4.1.tar.gz -O- |tar zxvf - cd tktreectrl-2.4.1/ ./configure --with-x --enable-shellicon --enable-gtk --enable-threads --prefix=/usr make sudo make install #or checkinstall
Topics: Linux | No Comments »
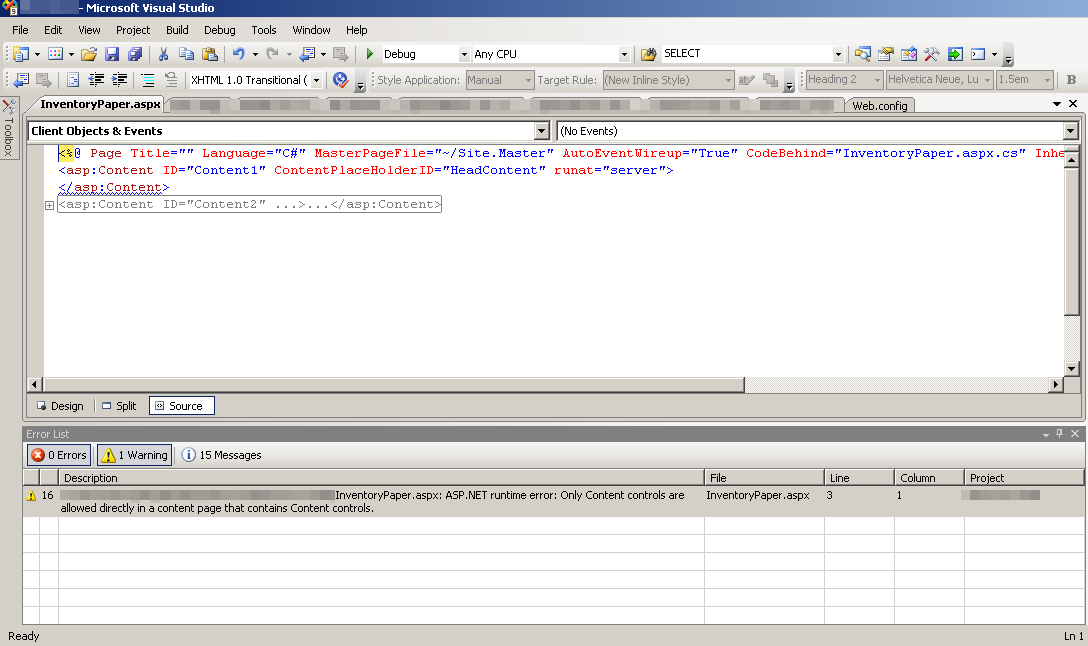
Solving “Only Content controls are allowed directly in a content page that contains Content controls”
By admin | February 3, 2012
While debugging and creating a new ASP.NET User Control, I stumbled across the following error, “Only Content controls are allowed directly in a content page that contains Content controls” that I did not encounter before. The culprit: an invalid assembly in the custom ASP.NET User Control registration section of “web.config“:
The first thing I tried, is, of course, to follow the advice on the can and remove any tag or text other than “<asp:Content>” tags from the page. But as, you can see, there are no other characters or tags on the page, and I had tried many times to regenerate the page or force VS to “re-parse” the page without success.
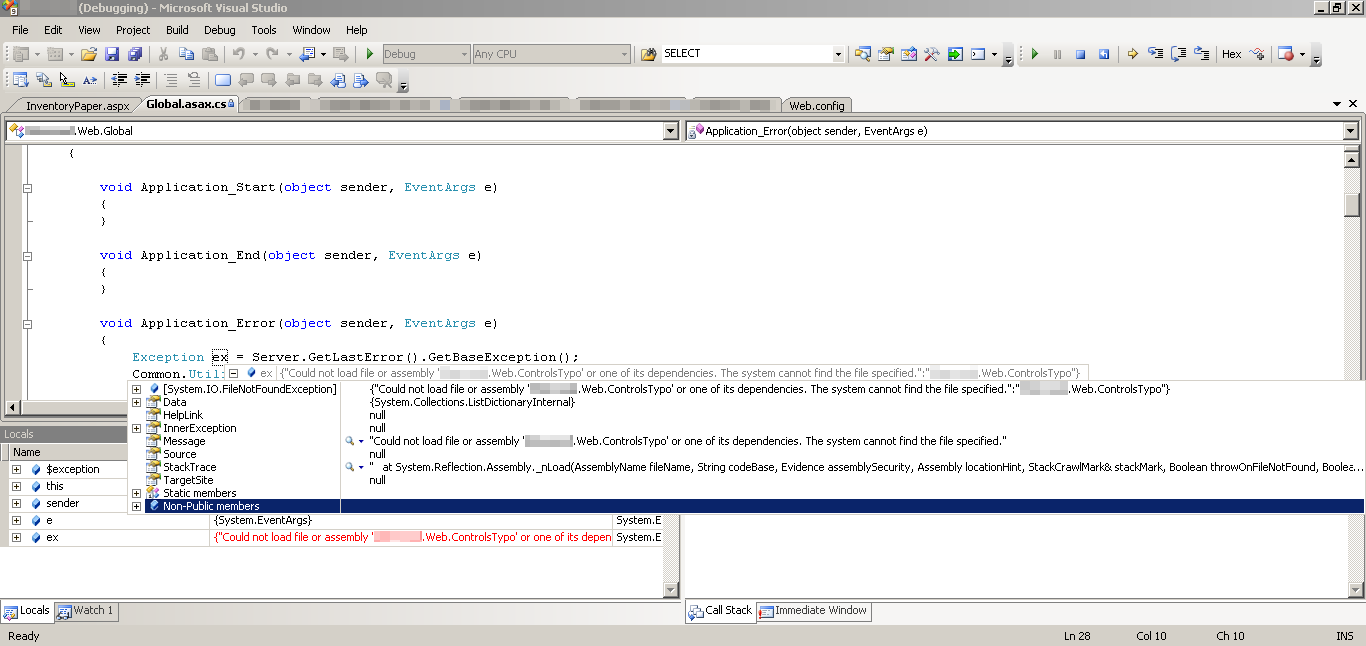
After some more debugging for a while, I found this error, which was related to an invalid assembly in the registering custom ASP.NET User Controls section of the web.config document:
And the answer? It turns out it was easy enough to fix after all, just fix the offending assembly reference!
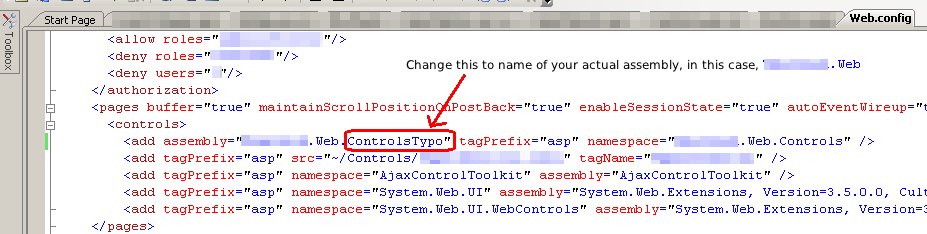
The culprit of the error, Only Content controls are allowed directly in a content page that contains Content controls
And voila, fixed:
Topics: Windows | 13 Comments »
Android codec benchmarks
By admin | February 1, 2012
VLC for Android pre-alpha benchmarks (Feb 1, 2012) for various audio codecs.
Skip to
Specs
Motorola XT300 – Android 2.1, 500 Mhz, 256 MB, rooted with busybox, Qualcomm MSM7225 (ARM1136EJ-S core, ARMv6TEJ architecture, no NEON extensions)
/proc/cpuinfo output
Processor : ARMv6-compatible processor rev 2 (v6l) BogoMIPS : 525.92 Features : swp half thumb fastmult edsp java CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 6TEJ CPU variant : 0x1 CPU part : 0xb36 CPU revision : 2 Hardware : QCT MSM7x25 SURF Revision : 0000 Serial : 0000000000000000
Method
adb shell "/system/xbin/busybox ps aux | grep vlc" adb shell "/system/xbin/busybox top -b | grep <pid of VLC as above>"
Ogg files
Comparing three popular codecs for decoding OGG vorbis files, libavcodec from libav, vorbis and tremor.
Results
PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND avcodec: 5266 956 10072 S 163m 88.4 0 25.0 org.videolan.vlc.android vorbis: 5331 956 10072 R 166m 89.8 0 41.0 org.videolan.vlc.android tremor: 5174 956 10072 S 156m 84.5 0 32.4 org.videolan.vlc.android
So, it seems avcodec is the clear winner, followed by tremor and lagging in last place libvorbis.
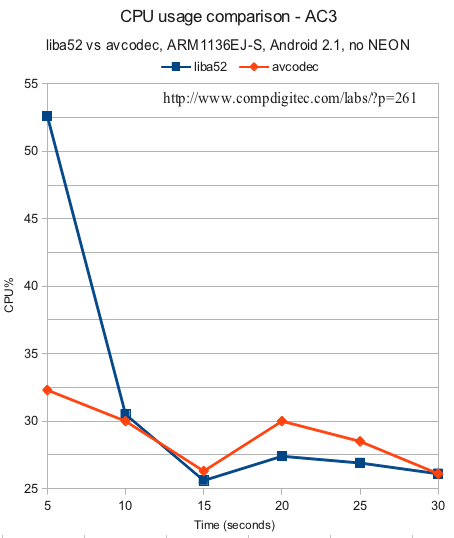
AC3 files
Test sample
First 30 seconds of http://people.videolan.org/~jb/ac3_the_other_side_44khz.wav
Results – Inconclusive?
| liba52 Mean: 31.51667% Median: 27.15% |
libavcodec Mean: 28.86667% Median: 29.25% |
ac3 with liba52
-A dummy --codec=a52tofloat32 D/vlc ( 6768): using decoder module "a52" Over 30 seconds PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 6768 956 10072 R 160m 86.7 0 52.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 6768 956 10072 S 159m 86.1 0 30.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 6768 956 10072 R 156m 84.5 0 25.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 6768 956 10072 S 156m 84.5 0 27.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 6768 956 10072 S 156m 84.5 0 26.9 org.videolan.vlc.android 6768 956 10072 S 156m 84.5 0 26.1 org.videolan.vlc.android Mean: 31.51667 Median: 27.15 Mode: N/A
ac3 with libavcodec
-A dummy --codec=avcodec D/vlc ( 6829): using decoder module "avcodec" Over 30 seconds PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 6829 956 10072 S 158m 85.5 0 32.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 6829 956 10072 R 155m 83.8 0 30.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 6829 956 10072 S 155m 83.8 0 26.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 6829 956 10072 S 155m 83.8 0 30.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 6829 956 10072 S 155m 83.8 0 28.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 6829 956 10072 S 155m 83.8 0 26.1 org.videolan.vlc.android Mean: 28.86667 Median: 29.25 Mode: 30.0
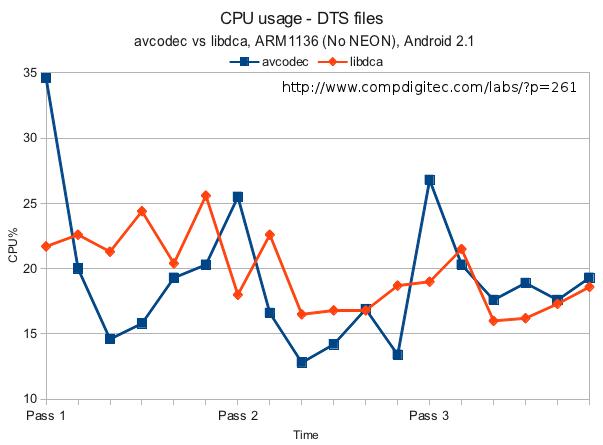
DTS files
Test sample
First 35 seconds of http://people.videolan.org/~jb/dts_the_other_side_44khz.wav
Results – Also inconclusive?
| libdca Mean: 19.66% Median: 18.85% Mode: 22.60%, 16.80% |
libavcodec Mean: 19.13% Median: 18.25% Mode: 19.3%, 20.3%, 17.6% |
dts with libdca
-A dummy --codec dts Mean: 19.66 Median: 18.85 Mode: 22.60,16.80 Pass 1: D/vlc ( 2461): using decoder module "dts" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2461 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 21.7 org.videolan.vlc.android 2461 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 22.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2461 951 10072 R 159m 86.3 0 21.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 2461 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 24.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 2461 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 20.4 org.videolan.vlc.android 2461 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 25.6 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 2: D/vlc ( 2510): using decoder module "dts" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.6 0 18.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.6 0 22.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.5 0 16.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.5 0 16.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.6 0 16.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 2510 951 10072 S 158m 85.6 0 18.7 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 3: D/vlc ( 2536): using decoder module "dts" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2536 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 19.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 2536 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 21.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 2536 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 16.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 2536 951 10072 R 159m 86.3 0 16.2 org.videolan.vlc.android 2536 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 17.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 2536 951 10072 S 159m 86.3 0 18.6 org.videolan.vlc.android
dts with libavcodec
-A dummy --codec avcodec Mean: 19.13 Median: 18.25 Mode: 19.3, 20.3, 17.6 Pass 1: D/vlc ( 2583): using decoder module "avcodec" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2583 951 10072 S 162m 87.5 0 34.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2583 951 10072 S 157m 85.4 0 20.0 org.videolan.vlc.android 2583 951 10072 S 158m 85.4 0 14.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2583 951 10072 R 158m 85.4 0 15.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 2583 951 10072 S 158m 85.4 0 19.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 2583 951 10072 S 157m 85.4 0 20.3 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 2: D/vlc ( 2607): using decoder module "avcodec" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2607 951 10072 S 159m 86.4 0 25.5 org.videolan.vlc.android 2607 951 10072 S 156m 84.8 0 16.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2607 951 10072 S 156m 84.8 0 12.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 2607 951 10072 S 156m 84.8 0 14.2 org.videolan.vlc.android 2607 951 10072 S 156m 84.8 0 16.9 org.videolan.vlc.android 2607 951 10072 R 157m 84.8 0 13.4 org.videolan.vlc.android Pass 3: D/vlc ( 2633): using decoder module "avcodec" PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %MEM CPU %CPU COMMAND 2633 951 10072 S 158m 85.8 0 26.8 org.videolan.vlc.android 2633 951 10072 S 158m 85.8 0 20.3 org.videolan.vlc.android 2633 951 10072 R 158m 85.8 0 17.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2633 951 10072 S 158m 85.8 0 18.9 org.videolan.vlc.android 2633 951 10072 S 158m 85.8 0 17.6 org.videolan.vlc.android 2633 951 10072 S 158m 85.8 0 19.3 org.videolan.vlc.android
Topics: Mobile | 12 Comments »
Deepen an existing shallow clone with git
By admin | January 31, 2012
In git, the new revolutionary DVCS system, to shallow clone a repository means to check out only the latest snapshot of a git repository, unlike a normal clone which pulls the entire repository. A shallow git repository can save bandwidth and take up less space.
git clone --depth=1 git://repo.example.com/mycoolapp
However, let’s say that once you checkout the project, compile it and decide that you want to contribute to it, then a shallow clone would probably not suffice. In this case, one can deepen the repository by using the following command inside the git repository, where n = number of revisions to deepen to:
git fetch --depth=n origin master
Saves more than having to re-clone everything from scratch and lose your working tree.
Topics: Linux | 13 Comments »